RSU or Restricted Inventory Models are shares of the corporate given to workers freed from price however with some restrictions. What are RSUs? Why are RSUs given? What’s the vesting date? When are RSU taxed? Is there a capital achieve on promoting RSU? What’s the capital achieve from promoting RSU? We will reply these questions by speaking concerning the RSU of an American MNC.
Overview of RSU, Tax, and ITR
RSU or Restricted Inventory Models are shares of the corporate given to worker freed from price however with some restrictions(because the identify suggests)
- On Granting of RSU no tax implication. It’s only a promise by the employer
- On the vesting day, the given proportion of RSUs are transferred to worker’s buying and selling account.
- Worker has to pay tax primarily based on his revenue slab.
- the worth of shares is taken into account as Perquiste in India and seems in Type 16. The market worth of the shares vested (variety of shares vested x Truthful Market worth X Conversion from Greenback to Indian Rupee) is added to the worker’s taxable revenue as perquisites. The worth at which Inventory is given to you is named because the Truthful Market Worth
- Tax is likely to be deducted within the different nation.
- US MNCs with workers in India typically submit W-8BEN to US brokers to keep away from any withholding associated to US taxes.
- Indian firms deduct % of shares as tax.
- There may be no double taxation as tax is paid from the sale of shares.
- One must declare shares acquired as RSU as Capital Asset in Schedule FA(Overseas Property) of ITR2, ITR3, ITR4.
- ITR1 does NOT have the schedule for Overseas Property. So when you RSU, ESPP in MNC you can’t file ITR1.
- It is best to fill in details about all of the RSUs you could have as of the monetary yr of the MNC
- It is best to present revenue you derived from it(Dividend, Capital Positive factors).
- If tax for RSU has been deducted by promoting of shares, Variety of shares talked about needs to be after the deduction. So if 100 shares bought vested and 30 shares had been deducted then you could present solely 70 shares in Overseas Property.
- One can solely promote the RSUs which are vested. On the sale of the vested shares, the revenue earned is a capital achieve and is due to this fact taxable in India.
- For RSUs, the distinction between the vesting worth or the Truthful Market Worth and the sale worth is the as capital achieve
- For RSUs, the acquisition date is the vesting date.
- Because the RSUs of the MNCs aren’t listed on the Indian inventory trade and no STT(Safety Transaction Tax) is paid so the definition of a long run and short-term capital good points is totally different from the shares listed on Indian inventory trade like BSE and NSE.
- Brief-term capital property – when offered inside 24 months of holding them. Brief-term good points are taxed at worker’s revenue tax slab charges
- Lengthy-term capital property – when offered after 24 months of holding them. Lengthy-term good points are taxed at 12.5% (earlier than Lengthy-term good points are taxed at 20% with indexation earlier than Funds 2024)
- This capital achieve should be declared in Schedule CG of ITR2 ITR3, ITR4 for tax functions.
- Advance Tax needs to be paid for revenue/capital achieve of greater than 10,000 Rs.
The reporting can be as beneath for overseas shares on
- Schedule CG for Capital achieve on Sale of Shares
- Schedule OS for Dividend revenue
- Schedule FSI and Schedule TR for claiming the overseas tax credit score in case of double taxation aid
- Schedule FA: Particulars of holding of overseas shares/securities
RSU or Restricted Inventory Models
RSU or Restricted Inventory Models are shares of the corporate given to worker freed from price however with some restrictions(because the identify suggests). The restriction is that although an worker is granted RSUs on a selected day (akin to when he joins an organization or will get a promotion) he will get possession of the shares over a time frame. It’s an incentive to the worker to remain within the firm and to revenue from the expansion of the corporate. When the shares are awarded to the worker in response to the schedule, it’s thought of as perquisite revenue and added to common revenue. When one sells the RSUs one capital achieve comes into play and one might need to pay tax relying on the interval of holding of RSU. Phrases related to RSU.
- Grant date: The date on which the shares are allotted
- Vesting date: the date on which the shares get transferred to the worker.
Say if one is granted 100 RSUs to be vested over 3 years within the ratio 34%/33%/33% on 23 Nov 2023. Then 34 RSUs (34%) will vest on 23 Nov 2024 and 33 every (33%) on 23 Nov 2025 and 23 Nov 2026 respectively. In case you go away the corporate on 1 December 2025, then it is possible for you to to promote solely 34 shares and the remaining 66 shares will return to the corporate. In case you stick round for one more month, then it is possible for you to to promote 67 shares (34 + 33) as one other 33 shares will vest on 23 Nov 2025.
So if one is granted 100 RSUs to be vested over 4 years within the ratio 25%/25%/25%/25% on 16 Dec 2023. Then 25% of RSUs i.e 25 shares of the corporate will vest on 16 Dec 2024, on 16 Dec 2025, 16 Dec 2026 and 16 Dec 2027 respectively. (If the vesting day is vacation then the shares vest on subsequent working day)
The opposite form of incentives supplied by the businesses are ESPP and ESOP.
Our article What are Worker Inventory Choices (ESOP) explains ESOP intimately.
Our article Worker Inventory Buy Plan or ESPP explains ESPP intimately.
Tax when RSUs are Granted
On Granting of RSU no tax implication. It’s only a promise by the employer.
Tax when RSUs are Vested
Vesting date is the date on which the predefined proportion of shares get transferred to the worker in response to the predefined schedule. Say one is granted 100 RSUs to be vested over 4 years within the ratio 25%/25%/25%/25% on 16 Dec 2023. Then 25% of RSUs i.e 25 shares of the corporate will vest on 16 Dec 2024. On the vesting day, the given proportion of RSUs are transferred to worker’s buying and selling account, for instance, eTrade or Charles Schwab account for an American MNC. On Vesting, one has to maintain following issues
- one has to pay tax primarily based on revenue slab.
- the worth of shares is taken into account as revenue in India.
Tax on RSU
Corporations are obligated to deduct taxes for RSUs vested. The most typical technique of deducting tax is share withholding, the place the corporate withholds sufficient shares to cowl the tax legal responsibility and deposits internet shares to your brokerage account. This feature is named as Promote to cowl. Some firms allow different strategies, akin to money or sell-to-cover transactions, that are defined beneath. Completely different strategies could also be supported by buying and selling firms like Schwab or eTrade, however solely the strategies approved by your organization can be out there to you.
The assorted choices to deduct tax on broking website the place the RSUs are held are as follows:
- A sell-to-cover That is the default choice the place TDS (as per your revenue slab) proportion of the vested shares are offered instantly and the quantity is paid to the federal government as tax. The remaining 70% of the vested shares stay in your account and you’ll promote them later everytime you need. Actully tax deducted is as per the revenue slab however as in a lot of the firms, the RSUs are supplied above a sure stage the place revenue is available in 30% revenue slab.
- A same-day sale: All of the vested RSUs are offered instantly. Share of the sale proceeds are deducted and paid as tax to the federal government and the remainder of cash will get wired to your account. You don’t any shares after this.
- A money train permits you to pay the tax and no shares are offered. The cash to pay should be out there in your brokerage account.
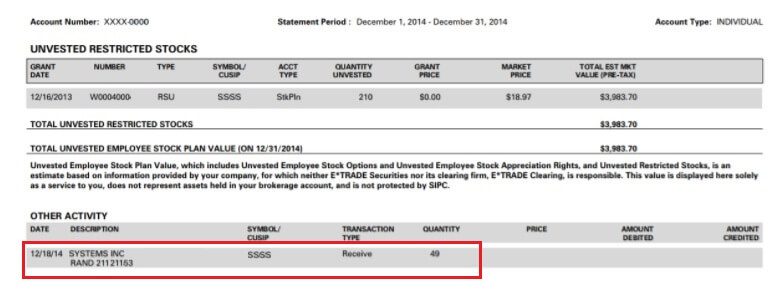
The default choice is Promote to Cowl therefore If 70 RSUs are vested you then would get solely 49 shares in your account on account of taxation. 30% of 70 = 21 which is taken as tax. So no of shares within the account turns into 70-21=49.
RSUs as Perquisite Earnings in India
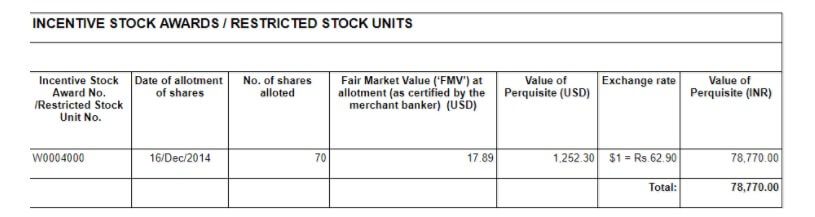
For RSUs, the acquisition worth or buy worth is zero and so your complete market worth of vested shares is handled as revenue in India as a perquisite. The market worth of the shares vested (variety of shares vested x Truthful Market worth X Conversion from Greenback to Indian Rupee) is added to the worker’s taxable revenue as perquisites. The worth at which Inventory is given to you is named because the Truthful Market Worth. All of the shares which are vested are used to calculate the Perquiste Earnings which incorporates the shares which had been offered for tax. if 70 RSUs are vested you then would get solely 49 shares in your account on account of taxation however all of the 70 shares can be used to calculate the perquiste revenue.
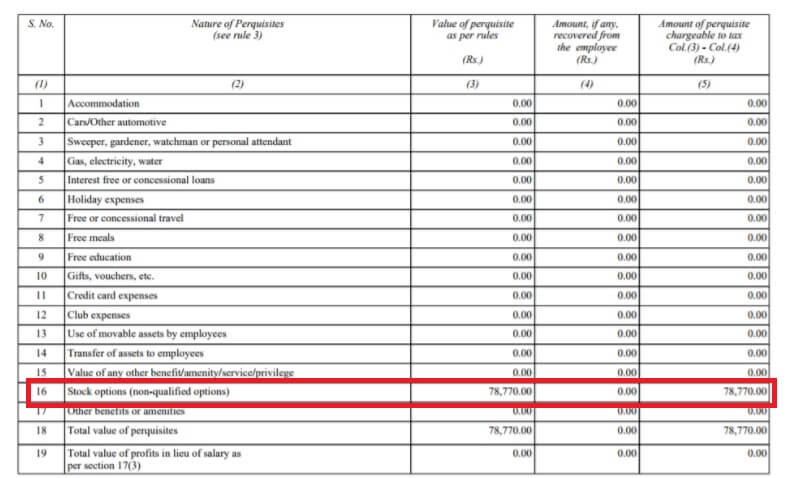
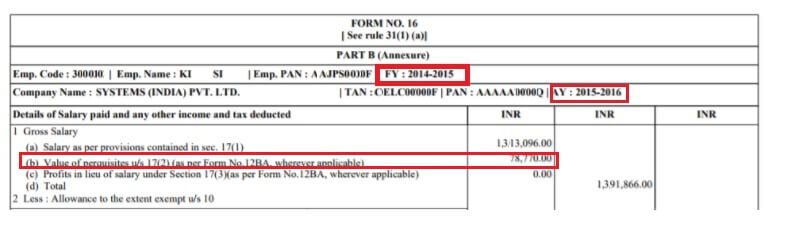
It’s declared in his Type 12BA for the yr and is obtainable in your Type 16, as proven within the pictures beneath. The Indian firm provides it to worker’s Earnings and costs Tax accordingly.
Our article Understanding Type 12BA give particulars of Perquisites given to an worker intimately.
Our article Understanding Type 16: Tax on revenue explains the Type 16. Earnings Tax Type 16 is a certificates from the employer which certifies that TDS has been deducted from worker’s wage by the employe
Are RSU’s Taxed Twice?
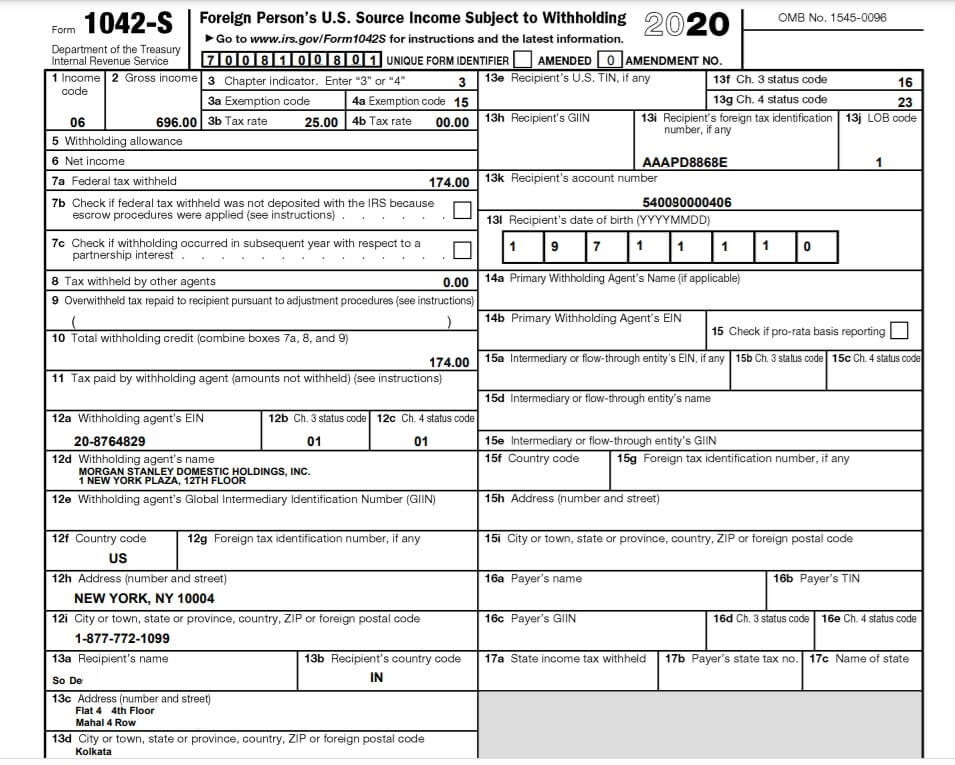
Brief Reply is RSU’s aren’t taxed twice. If they’d have been taxed twice you’d have Govt doc of the nation deducting tax saying that tax has been deducted. Like Type 16/Type 16A offered by Indian Govt or Type 1042-S offered by US when the tax is deducted on the dividend of US compnaies.
An worker (Resident Indian) working in India in a subsidiary of a US Firm is given RSU or Restricted Inventory Models of the father or mother firm.
When the shares are vested, some shares are withheld (Promote to cowl) to satisfy tax legal responsibility in US and after lowering these shares, the stability is given to the worker.
Indian firm additionally calculates prerequisite primarily based on FMV on the whole variety of shares together with withheld shares and TDS is deducted. That is mirrored in Type 16 Half B.
So are RSUs are taxed twice. About 65.22% worth is consumed in tax.
Is double taxation accomplished by the corporate is appropriate?
Can DTAA advantages be availed for a refund?
No, RSUs aren’t taxed twice is what my firm says. Simply since you are seeing that in your Type 16 and your brokers statements, it doesn’t imply that its been deducted twice.
Within the instance above, Reader Smriti defined superbly.
100* FMV was added to your prerequisite to point out it as part of revenue. it simply means you had been paid a 100*FMV quantity by the corporate( in type of shares).
66 shares are deposited to your brokerage account.
The remaining shares (100-66 = 34) are thought of to be offered by the dealer in your behalf and the quantity obtained from that is paid as tax.
All these calculations are a part of your wage prerequisite and therefore, will present in your wage slip because the tax you might be paying to Govt of India.
The employer will not be deducting tax twice. it’s simply including all the main points within the payslip.
We’ve got heard that Proof is within the pudding or present me the proof. If the tax had been deducted by the overseas firm then they should present paperwork like Type 16/Type 16A in India and Type 1042-S within the US. The Pattern Type 1042-S from our article How are Dividends of Worldwide or Overseas Shares taxed? The way to present in ITR is proven beneath.
Dividend revenue from overseas shares
Dividend revenue earned from overseas shares is taxed as per Earnings Tax slabs below the top Earnings from Different Sources.
In Schedule TR, you could present a abstract of tax aid that’s being claimed in India for taxes paid exterior India in respect of every nation. This schedule captures a abstract of detailed info furnished in Schedule FSI.
Within the case of sure ESOPs, a person may obtain dividend-equivalent revenue on unvested shares. These are typically taxed as a part of wage revenue.To find out one’s taxation it’s advisable to have a chat together with your Employer or colleagues.
The Double Taxation Avoidance Settlement or DTAA is a tax treaty signed between India and one other nation in order that taxpayers can keep away from paying double taxes on their revenue earned from the supply nation in addition to the residence nation. At current, India has double tax avoidance treaties with greater than 80 international locations around the globe.
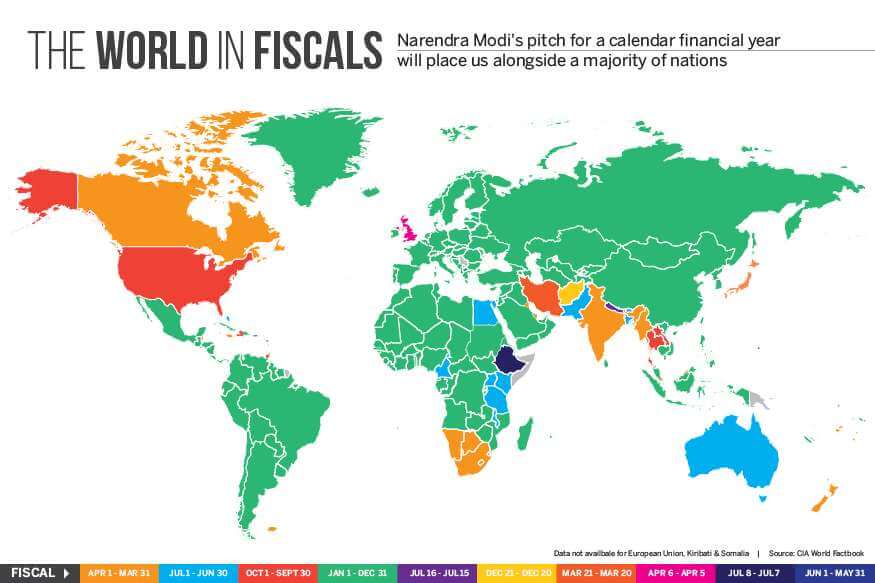
Monetary years of various international locations
“It’s hereby clarified {that a} taxpayer shall be required to reply the related query (whether or not overseas property are held or not) within the affirmative, provided that he has held the overseas property and so on. at any time in the course of the “earlier yr”(in India) as additionally at any time in the course of the “related accounting interval”(within the overseas tax jurisdiction), and refill Schedule FA accordingly.”
Lets take an instance of RSUs of a MNC headquartered in USA which has monetary yr from 1 Jan to 31 Dec. So solely RSUs(ESPPs) acquired between 1 Jan 2022 to 31 Dec 2023 must be reported.
Monetary years for standard international locations are given beneath
1. United States: Monetary yr is from January 1st to December thirty first.
2. United Kingdom: Monetary yr is from April sixth to April fifth.
3. Canada: Monetary yr is from January 1st to December thirty first.
4. Australia: Monetary yr is from July 1st to June thirtieth.
5. United Arab Emirates: Monetary yr is from January 1st to December thirty first.
For particulars checkout our article Distinction between Evaluation Yr and Monetary Yr, Earlier Yr,Fiscal Yr in World
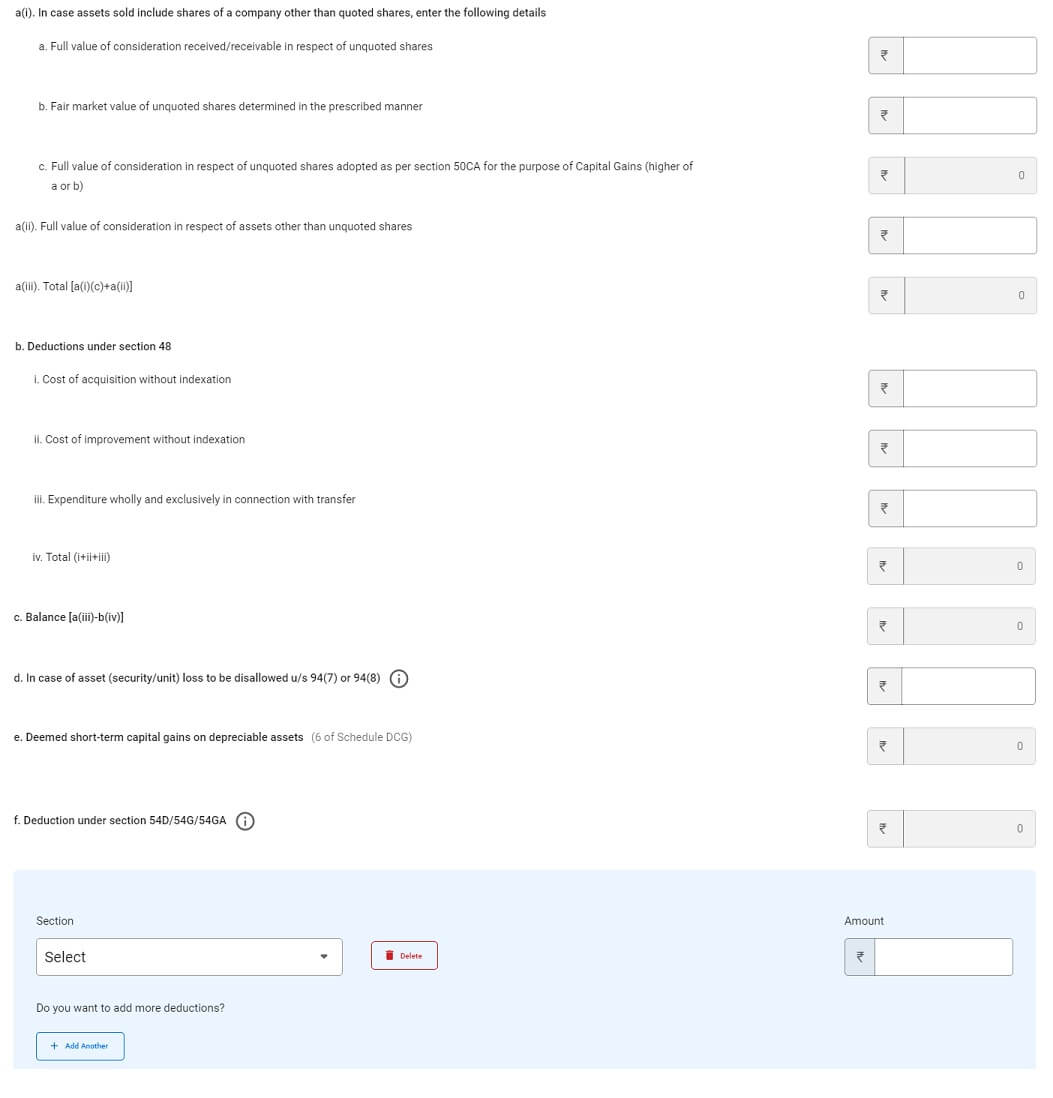
The way to present RSU, ESPP, and Overseas Property in ITR
One wants to point out shares acquired as RSU(ESPP/ESOP) as Capital Asset in Schedule FA(Overseas Property) of ITR aside from ITR1 akin to ITR2, ITR3, ITR4 as proven within the picture beneath. ITR1 does NOT have the schedule for Overseas Property.
The picture beneath exhibits the case of solely when shares of an organization within the US had been allotted to the worker and the worker has not offered them until submitting of the revenue tax return. To fill this please undergo Perquisite on Inventory Choices report and the break up offered by your employer on shares allotted to you.
If tax for RSU has been deducted by promoting of shares, the Variety of shares talked about needs to be after the deduction. So if 100 shares bought vested and 30 shares had been deducted then you could present solely 70 shares in Overseas Property. Complete Funding values is the Variety of shares in your account X Truthful Market Worth X US greenback inventory worth.
When you’ve got bought RSU at totally different occasions and also you haven’t offered them then particulars about every allotment you had until 31 Mar of the monetary yr for which you might be submitting ITR needs to be put within the Overseas Property desk.
For instance, your 70 RSUs bought vested in 2020 and 70 in 2021, the details about each the allotments needs to be in Overseas Property.
Schedule for Overseas Earnings in ITR
Distinction between Schedule Overseas Supply Earnings (FSI) and Overseas Property (FA)
Is Schedule FSI required to be crammed in ITR2?
I’m resident in India. I’ve been allotted inventory choices (of my father or mother US firm), which have been proven in my Type 16. Do I additionally want to point out this revenue in Schedule FSI or Schedule FA (Overseas Property)? No Tax has been deducted within the US and I’m not claiming any refund.
- In Schedule Overseas Supply Earnings (FSI), you could report the main points of revenue, which is accruing or arising from any supply exterior India. FSI schedule is obligatory for residents who earned revenue from exterior India and tax paid exterior India and to say the good thing about DTAA on such revenue.
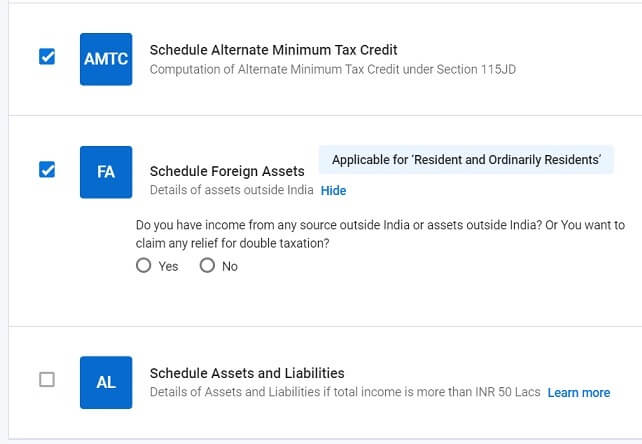
The way to choose the Schedules?
Go to Schedule Choice
- Click on Earnings to see the Earnings from Capital Positive factors Schedule. Choose the Schedule
- Click on Earnings to see the Overseas Supply Earnings schedule. Choose the Schedule
- Click on Others to see the Overseas Property Earnings schedule. Choose the Schedule
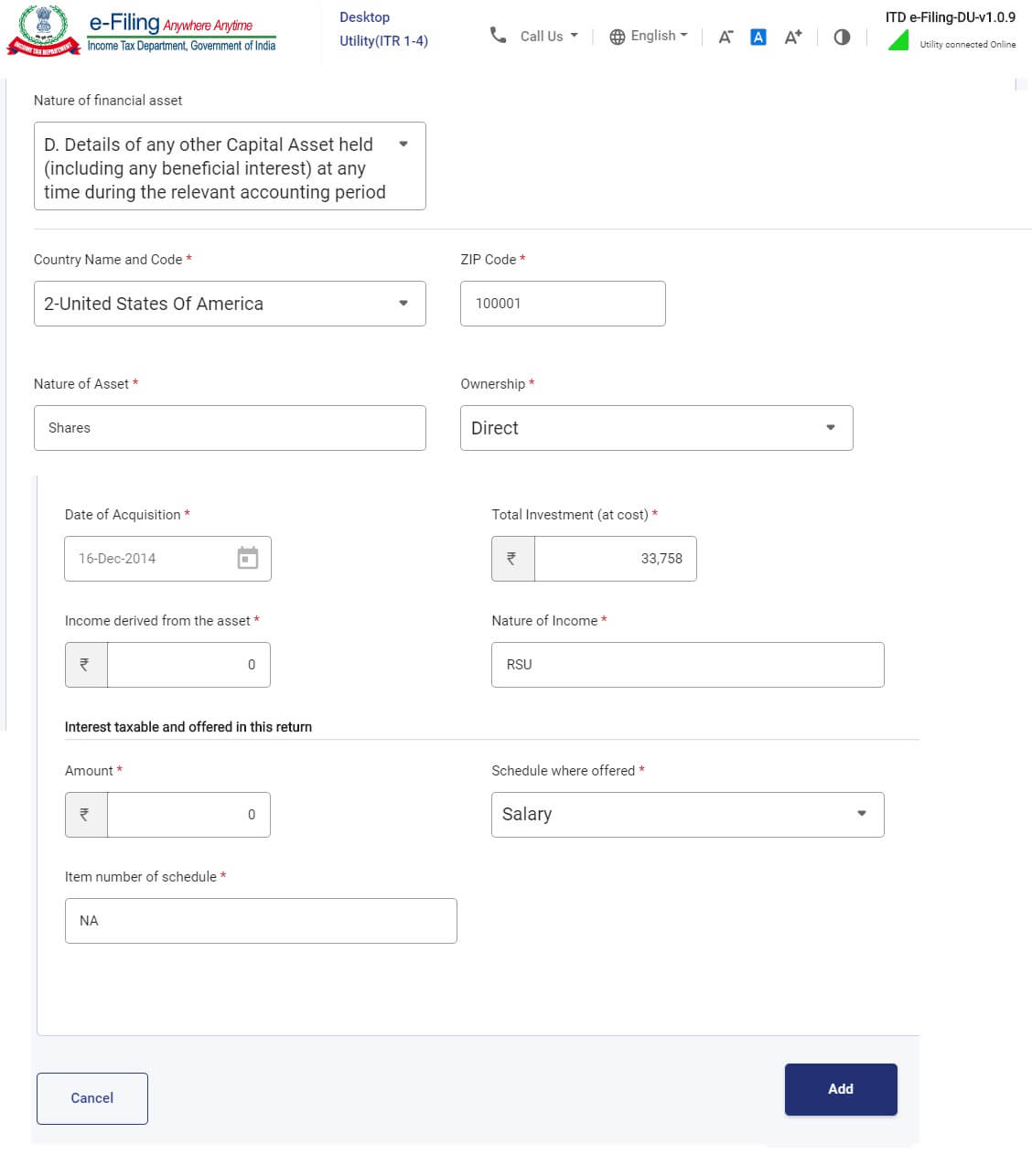
Particulars to be crammed in Overseas Asset schedule in ITR2
Particulars to be crammed are:
- Nation Title and code: The Nation the place the trade on which shares are listed is traded. Ex for somebody working in Amazon or Microsoft, it could be the USA. Code is obtainable within the dropdown in ITR.
- Nature of asset: Shares
- Nature of Curiosity-Direct/Useful/proprietor/Beneficiary: Direct
- Date of acquisition: Date on which shares had been allotted
- Complete Funding (at price) (in rupees): Value at which RSU/ESPP was allotted. (Please deduct the variety of shares that had been credited to your account after-tax deduction. Say you had been allotted 70 shares however due to tax solely 49 shares had been credited into your broking account). In instance 49*17.89(FMV)*62.90(USD Alternate charge)
- Earnings accrued from such :
- 0, when you haven’t offered the shares.
- When you’ve got earned a dividend then declare the dividend acquired.
- When you’ve got offered the shares then it’s a must to present the revenue/loss acquired from the sale of the shares.
- Nature of Earnings: What sort of Earnings it’s. For Overseas shares not offered it’s Earnings from Wage. For Overseas shares offered it’s revenue from Capital Positive factors.
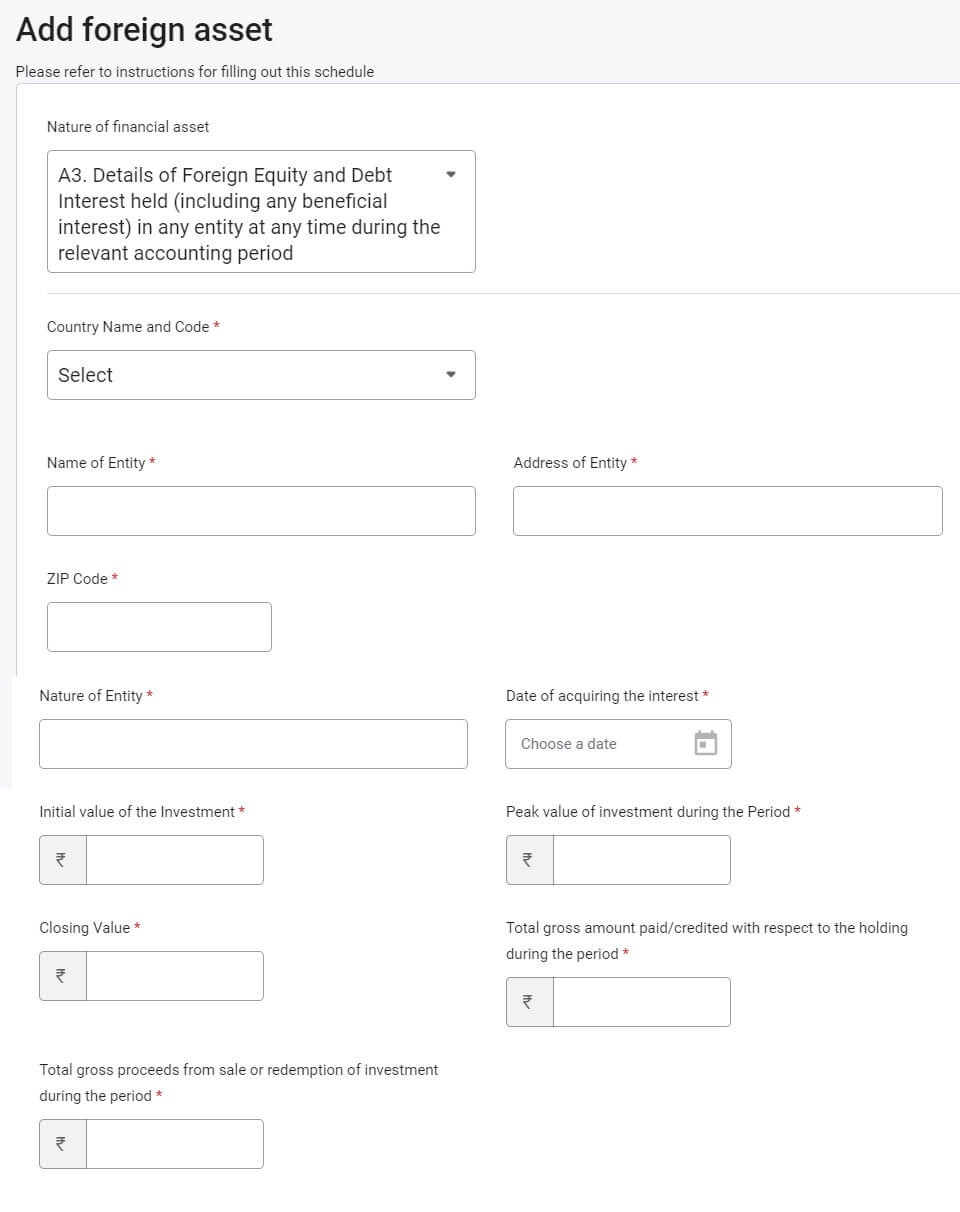
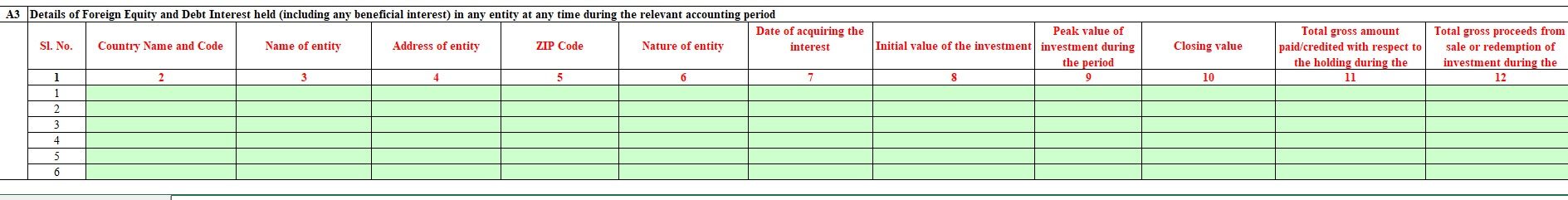
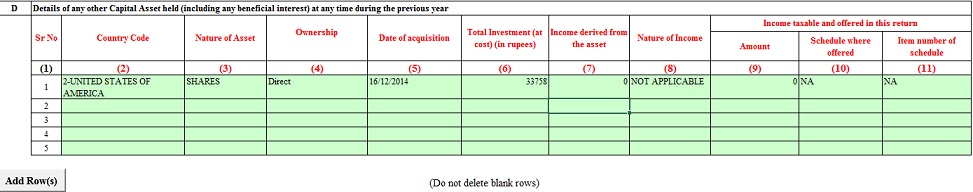
Desk A3 or Desk D
You possibly can declare it in Desk A3 or Desk D of Overseas Property as proven within the pictures beneath
Technically it needs to be declared in Desk A3. Additional particulars required in Desk A3 are the Peak Worth of funding in the course of the interval, Closing Worth. Closing Worth needs to be as of 31 Mar. These particulars yow will discover out of your dealer.
In desk A3, the preliminary worth of the funding, the height worth of the funding in the course of the accounting interval, the closing worth of the funding as on the finish of the accounting interval, gross curiosity paid, the whole gross quantity paid or credited to the account in the course of the accounting interval,and complete gross proceeds from sale or redemption of funding in the course of the accounting interval is required to be disclosed after changing the identical into Indian forex
However because it requires extra particulars, many individuals do it in Desk D, the rationale being we’re declaring the revenue and account for it.
 Desk A3 and Desk D within the outdated ITR
Desk A3 and Desk D within the outdated ITR
Our article Are ESPP, ESOP in MNC to be filed in ITR as Overseas Property? discusses What are overseas property? The Overseas Asset schedule in ITR2.
Tax On Sale of RSU
One can solely promote the RSUs which are vested. On the sale of the vested shares, the revenue earned is a capital achieve and is due to this fact taxable in India.
For RSUs, the distinction between the vesting worth or the Truthful Market Worth and the sale worth is the capital good points.
Because the RSUs of the MNCs aren’t listed on the Indian inventory trade and no STT(Safety Transaction Tax) is paid so the definition of a long run and short-term capital good points is totally different from the shares listed on Indian inventory trade like BSE and NSE.
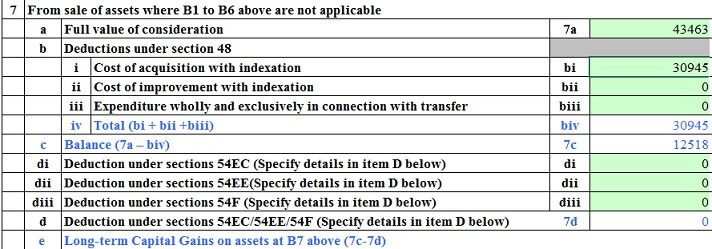
From FY 2016-17 i,e for the sale of unlisted shares on or after 1st April 2016 UNLISTED fairness shares is given beneath. This capital achieve should be declared in Schedule CG of ITR in order that tax could also be suitably charged
- short-term capital property – when offered inside 24 months of holding them. Brief-term good points are taxed at worker’s revenue tax slab charges
- long-term capital property – when offered after 24 months of holding them. Lengthy-term good points are taxed at 20% with indexation (so part 48 which makes use of Indexation applies)
The revenue tax Act in India act differentiates between the tax on capital good points of listed and unlisted shares.
- Listed shares are these which are listed on Indian inventory exchanges, akin to TCS, HDFC Financial institution, and so on.
- Unlisted shares are these that aren’t listed on Indian exchanges, no matter whether or not they’re of Indian firms or overseas firms listed on overseas exchanges akin to Google, Microsoft, Apple, and so on.
The tax remedy on capital good points which are unlisted in India or listed out of India is similar. So when you personal shares of an American firm, this firm will not be listed in India, therefore it’s thought of unlisted for the aim of taxes in India.
The interval of holding begins from the vesting date as much as the date of sale
The desk beneath exhibits the instance of Brief Time period Capital Achieve and Lengthy-term Capital Achieve
| On the time of | Models | Date | FMV of share(USD) | Tax to be paid | In revenue tax return |
| Grant | 240 | 12-Dec-13 | Not Relevant | nil | Not Relevant |
| Vesting | 70 Vested
49 transferred |
12-Dec-14 | 17.89
1 USD = 62.90 Rs CII of yr 240 |
Tax of 30% taken by promoting 21 shares
Earnings Tax = 70 * 17.89* 62.90=78770 |
Perquiste Earnings as Earnings from Wage.
Taxed as per worker’s Earnings Tax Slab Fee |
| Sale of shares if unlisted | 20 | 31-Jul-15 | 20.96
1 USD = 63.60 Rs |
Brief Time period Capital Achieve= 20* ((63.60*20.96)-(62.90* 17.89))= Rs 4,155.5 | Beneath Capital Positive factors (quick time period capital good points)
Taxed as per Earnings Tax slab of worker |
| Sale of shares if unlisted | 25 | 31-Jan-17 | 25.89
1USD = 67.15 CII of the yr 264 |
Listed bought price = 62.90 * 264/240 = 69.19
Lengthy-Time period Capital Achieve with indexation= 25*((67.15 * 25.890)-(69.19* 17.89)) = =25* (1738.5135 -1237.8091) = 25*500.7044=12517.61 Lengthy-Time period Capital Achieve tax(with indexation) = 20% of 12517.61=2503.522 |
Beneath Capital Positive factors (long run capital good points)
Lengthy-Time period Capital Achieve with out indexation= 25*((67.15 * 25.890)-(62.90* 17.89)) = 15330.8125 Lengthy-Time period Capital Achieve tax(with out indexation) = 20% of 15,330.8125=3066.1625 |
Capital Loss
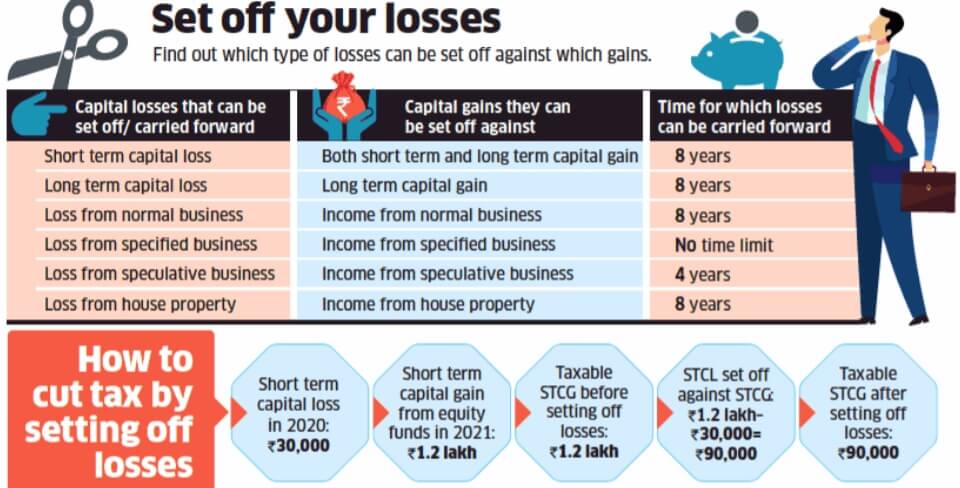
What if there’s loss on promoting shares? Fortunately Earnings Tax Division offers good thing about Setting of Capital Loss.
Set-Off Losses means adjusting the loss towards the taxable revenue earned; after that, remaining the loss may be carried ahead to future years.
The taxpayer can’t carry ahead losses to future years if the revenue tax return for the yr by which loss is incurred will not be filed on the Earnings Tax Web site inside the due date as per Sec 139(1).
If one has Brief time period capital loss, then it may be set off towards short-term or long-term capital achieve from any capital asset(actual property, gold, debt mutual funds).
If the loss will not be set off fully, then it may be carried ahead for a interval of 8 years and adjusted towards any short-term or long-term capital good points made throughout these 8 years. However provided that he has filed his revenue tax return inside the due date.
Exhibiting Capital Positive factors in ITR
Half A of the Capital Positive factors Schedule supplies for computation of quick‐time period capital good points (STCG) from the sale of several types of capital property. Out of this, merchandise No. A3 and A4 are relevant just for non‐residents.
Half B of this Capital Positive factors Schedule supplies for the computation of lengthy‐time period capital good points (LTCG) from the sale of several types of capital property. Out of this, merchandise No. B5, B6, B7, and B8 are relevant just for non‐residents
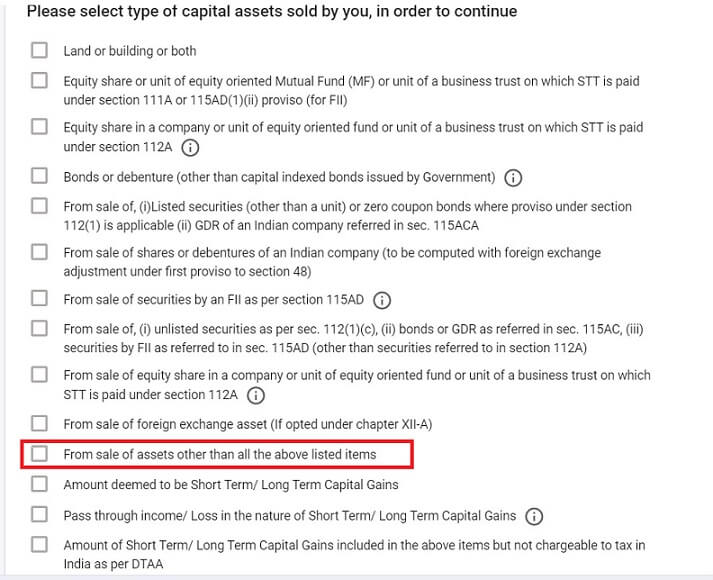
Select the Schedule Capital Positive factors
In Capital Achieve Schedule on the market of shares of MNC not listed on Indian Inventory Alternate select Sale of Property aside from listed. (along with another capital achieve you’d have)
Then Select Brief Time period Achieve/Lengthy Time period Achieve
- Brief Time period Achieve when you held shares for lower than 24 months
- Lengthy Time period Achieve when you held shares for greater than 24 months
The brand new ITR Utility exhibits the main points that should be crammed for Capital Positive factors
Capital Positive factors in Outdated ITR
Setting of the Capital Loss
When you’ve got a capital loss then in abstract you’d see the loss an instance of which is proven within the picture beneath. If there’s a Capital Loss, it could be mirrored as a unfavourable worth
Click on on Schedule CYLA (Present Yr Losses Changes). The main points entered in Capital Achieve Schedules will replicate in Set-Off/ Carry Ahead Schedules.
Be aware: Set off & carry Ahead Schedules will fetch information from Capital achieve Schedule. The taxpayer needn’t enter the main points once more in these schedules.
Click on on Schedule CFL (Carry Ahead Losses)
The unadjusted losses of that monetary yr can be carried ahead.
Within the following years ITR you may alter your capital good points towards this loss and cut back your tax legal responsibility.
DTAA and RSU
Double taxation refers back to the state of affairs when a person is taxed greater than as soon as on the identical revenue, asset or monetary transaction.The Double Tax Avoidance Agreements (DTAA) is bilateral agreements entered into between two international locations, in our case, between India and one other overseas state. The fundamental goal is to keep away from, taxation of revenue in each the international locations (i.e. Double taxation of similar revenue) and to advertise and foster financial commerce and funding between the 2 international locations.
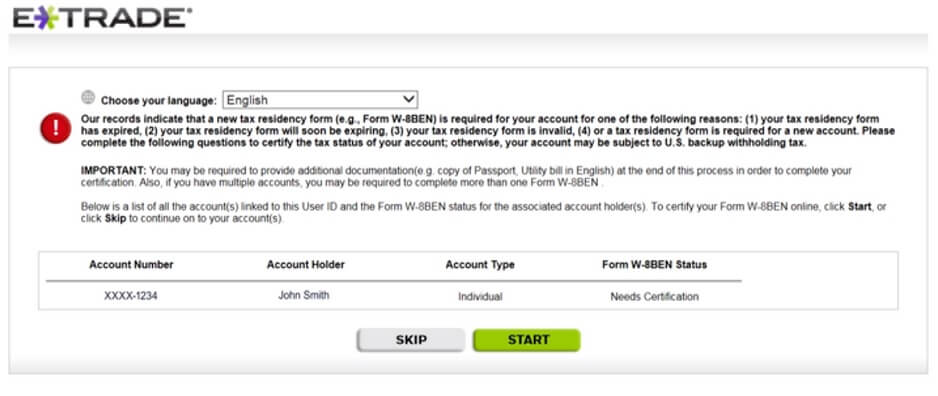
US MNCs with workers in India typically submit W-8BEN to US brokers to keep away from any withholding associated to US taxes. Nevertheless, the taxes and so on are deducted for the staff in India. These are reported in perquisites kind. (as defined above). The picture beneath exhibits how one has to certify W-8BEN kind on ETrade for US. Extra particulars within the video right here.
If any tax is deducted in US then US IRS division will ship Type much like Type 16 to your deal with.
Advance Tax on Capital Achieve of RSU
Advance Tax guidelines require that one’s tax dues (estimated for the entire yr) should be paid upfront. Advance tax is paid in installments. Whereas the employer deducts TDS when your RSUs get vested, one might need to deposit advance tax if one earns capital good points.
Non-payment or delayed fee of advance tax leads to penal curiosity below sections 234B and 234C.
You have to pay Advance Tax on RSUs solely once you promote the RSUs and the revenue is greater than 10,000 Rs. You have to pay an acceptable proportion of it earlier than the closest due date. So when you offered between 16 June and 15 Sep you could pay 45% earlier than 15 Sep.
| Due Date | Advance Tax Payable |
|---|---|
| On or earlier than fifteenth June | 15% of advance tax much less advance tax already paid |
| On or earlier than fifteenth September | 45% of advance tax much less advance tax already paid |
| On or earlier than fifteenth December | 75% of advance tax much less advance tax already paid |
| On or earlier than fifteenth March | 100% of advance tax much less advance tax already paid |
Nevertheless, it might be onerous to estimate tax on capital good points and deposit advance tax within the first few installments if a sale happened later within the yr. Subsequently when advance tax installments are being paid, no penal curiosity is charged the place installment is brief on account of capital good points. Remaining installment (after the sale of shares) of advance tax each time due should embrace the tax on capital good points.
Relying on the time period between the vesting date and the sale date, the revenue can both qualify for short-term or long-term capital good points tax. For RSUs, the acquisition date is the vesting date.
Our article Advance Tax:Particulars-What, How, Why is about Advance Tax for people.
Disclaimer: This info is for instructional functions solely. We’ve got tried to supply the data to one of the best of our potential. However please seek the advice of your CA, tax guide. Bemoneyaware.com will not be chargeable for any legal responsibility on info offered on the location.
Associated Articles:
- Wage, Internet Wage, Gross Wage, Price to Firm: What’s the distinction
- Wage, Allowances, Dearness Allowance, Authorities Wage, Pay Fee
- Understanding Variable Pay
- Understanding Type 16: Half I
- How To Fill Wage Particulars in ITR2, ITR1
- HRA Exemption, Calculation, Tax, and Earnings Tax Return
- How are Dividends of Worldwide or Overseas Shares taxed? The way to present in ITR
Hope this text helped in understanding What are RSUs? Why are RSUs given? What’s the vesting date? When are RSU taxed? Is there a capital achieve on promoting RSU? What’s the capital achieve from promoting RSU? The way to present these in ITR