Since we started the Fashionable Financial Principle (MMT) mission within the mid-Nineteen Nineties, many individuals have asserted (wrongly) that the evaluation we developed solely applies to the US as a result of it’s thought of to be the reserve forex. That standing, the story goes, implies that it might probably run fiscal deficits with relative impunity as a result of the remainder of the world clamours for the forex, which suggests it might probably at all times, within the language of the story, ‘fund’ its deficits. The corollary is that different international locations can not get pleasure from this fiscal freedom as a result of the bond markets will ultimately cease funding the federal government deficits in the event that they get ‘out of hand’. All of that is, in fact, fiction. Not too long ago, although, the US trade price has fallen to its lowest stage in three years following the Trump chaos and there are numerous commentators predicting that the reserve standing is underneath menace. In contrast to earlier intervals of world uncertainty when traders enhance their demand for US authorities debt devices, the present interval has been marked by a major US Treasury bond liquidation (notably longer-term property) because the ‘Trump’ impact results in irrational beliefs that the US authorities may default. This has additionally led to claims that the dominance of the US greenback in international commerce and monetary transactions is underneath menace. There are additionally claims the US authorities will discover it more and more tough to ‘fund’ itself. The fact is totally different on all counts.
All central banks maintain reserve currencies which permit them to make overseas trade transactions that affect the motion of trade charges.
Underneath the Bretton Woods system of fastened trade charges, the capability of a central financial institution to defend its forex towards depreciating forces trusted the amount of overseas reserves it held.
That proved to be a serious shortfall of the system and in the end led to its demise.
If a central financial institution didn’t have adequate portions of overseas forex reserves then it needed to search loans from the IMF underneath that system and/or devalue its forex underneath the Bretton Woods protocols.
With the versatile trade price system now dominating, central banks nonetheless keep overseas forex reserves for a spread of transactions together with the smoothing out of main forex actions.
The US greenback is the dominant reserve forex and nations maintain reserves of that forex to permit them to transact in commerce given {that a} important proportion of world commodity commerce is denominated within the US greenback.
Having shops of US {dollars} means a nation doesn’t must promote its personal forex for the US greenback so as to transact in international markets, which gives a modicum of stability to its personal forex.
The IMF publishes a dataset – Foreign money Composition of Official International Change Reserves (COFER) – which permits us to hint actions within the denomination of currencies held in reserve by central banks.
There are some technicalities – such because the distinction between allotted versus unallocated reserves – that we don’t have to enter right here.
This knowledge can also be related to a just lately launched a report from the European Central Financial institution (June 11, 2025) – The worldwide position of the euro – together with an in depth – Statistical Annex – which traces the “worldwide position of the euro”.
Any trace that the euro would turn into a dominant international forex shouldn’t be supported by the info, which reveals that the:
… share of the euro throughout numerous indicators of worldwide forex use has been largely unchanged, at round 19%, since Russia’s invasion of Ukraine. The euro continued to carry its place because the second most necessary forex globally.
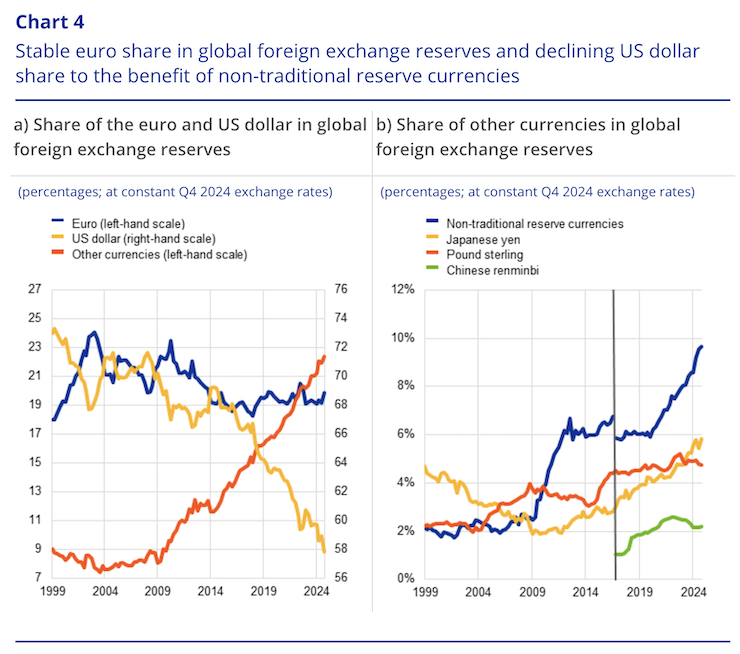
Whereas the “share of the US greenback” in “international official overseas reserves … declined by 2 proportion factors at fixed trade charges, to 57.8%” in 2024, the long term tendencies have seen the US greenback’s share decline by round 11 proportion factors during the last decade.
Within the March-quarter 1999, the US greenback share was 71.2 per cent.
By the December-quarter 2024, it had dropped to 57.8 per cent.
For different currencies (the IMF didn’t begin amassing this knowledge for all international locations on the identical time):
1. Euro – 18.1 per cent March-quarter 1999; 19.8 per cent December-quarter 2024.
2. Pound sterling – 2.7 per cent March-quarter 1999; 4.7 per cent December-quarter 2024.
3. Yen – 17.6 per cent March-quarter 1999; 19.8 per cent December-quarter 2024.
4. Yuan – 1.1 per cent December-quarter 2016; 2.2 per cent December-quarter 2024.
5. Canadian greenback – 1.4 per cent December-quarter 2012; 2.8 per cent December-quarter 2024.
6. Australian greenback – 1.5 per cent December-quarter 2012; 2.1 per cent December-quarter 2024.
The ECB present the next graph which reveals the shares of assorted currencies in international overseas trade reserves.
Being cautious to not be confused by way of the right- and left-hand scales, it’s clear that the US greenback has slipped fairly considerably and the “different currencies” have elevated their significance amongst establishments that maintain overseas trade reserves.
The “different currencies” embrace “the Canadian greenback, the Australian greenback, the Korean received, the Singapore greenback, the Swedish krona, the Norwegian krone, the Danish krone and the Swiss franc in lowering order of estimated significance”.
By way of the right-hand panel within the graph above, the ECB word that “By the top of 2024 the share of currencies aside from the US greenback and the euro had risen to 22.4%, pushed by robust positive aspects in non-traditional reserve currencies … its mixed share develop by 1.1 proportion factors in 2024, to 9.6%.”
Of curiosity is the truth that the Chinese language yuan (renminbi) initially was seen as a gorgeous reserve forex, its share peaking in 2022.
It has since declined and the latest report from OMFIF – World Public Investor 2024 – which research “international coverage and funding themes referring to central banks, sovereign funds, pension funds, regulators and treasuries”, discovered that:
… Urge for food for renminbi has soured. Practically 12% of reserve managers want to lower holdings within the subsequent 12-24 months.
Why?
That is partly as a consequence of relative pessimism on the near-term financial outlook in China, however the overwhelming majority additionally talked about market transparency (73%) and geopolitics (70%) as deterrents to investing in Chinese language monetary property.
Nevertheless, the longer-term tendencies are totally different.
The survey knowledge reveals that:
… over an extended horizon, central banks count on to diversify in direction of the renminbi. In web phrases, 20% anticipate including to their renminbi holdings over the subsequent 10 years, which is larger than for every other forex. On common, respondents anticipate that its share in international reserves will greater than double to five.6% within the subsequent decade, from 2.3% now.
However that may nonetheless not make it a dominant forex.
For each the euro and the renminbi, the worldwide roles performed by these currencies continues to be means underneath the dimensions of the respective economies, which provides folks licence to recommend that they may enhance their position in international reserves considerably over the subsequent a number of years.
There’s some opinion that Trump’s behaviour will speed up the development away from the US greenback.
ECB boss ‘Madame Lagarde’ launched the ECB Report saying:
… additional shifts could also be underway within the panorama of worldwide currencies. The tariffs imposed by the US Administration have led to extremely uncommon cross-asset correlations. This might strengthen the worldwide position of the euro and underscores the significance for European policymakers of making the required circumstances for this to happen. The primary precedence have to be advancing the financial savings and funding union to totally leverage European monetary markets. Eliminating boundaries throughout the EU is important to enhancing the depth and liquidity of euro funding markets, which is a precondition for a wider use of the euro. The deliberate issuance of bonds on the EU stage – as Europe takes cost of its personal defence – may make an necessary contribution to attaining these targets.
Be aware first, that the position of the euro in international overseas trade reserves has been invariant to the Russian invasion of the Ukraine, which some discovered stunning.
Lagarde is clearly making an attempt to situation the political debate in Europe in relation to the present arms’ race intentions.
However as I mentioned within the latest weblog posts – The arms race once more – Half 1 (June 11, 2025) – and – The arms race once more – Half 2 (June 12, 2025) – the European Fee’s technique is to sheet the elevated debt onto the Member States, which is not going to transform a profitable technique and may very well result in a reversal of any sentiment positive aspects with respect to the euro as a reserve forex.
Two components which may affect the demand by establishments for a selected forex as a reserve are: (a) trade price fluctuations, and (b) altering bond yields throughout nations. The second issue is much less of an element as a result of yields have a tendency to maneuver in live performance with financial fluctuations.
Nevertheless, in relation to the primary affect, an IMF report analysing the COFER knowledge (Might 5, 2021) – US Greenback Share of World International Change Reserves Drops to 25-12 months Low – discovered that fluctuation within the US greenback since 1999 explains “80 per cent of the short-term (quarterly) variance within the US greenback’s share of world reserves” and the “remaining 20 % of the short-term variance could be defined primarily by lively shopping for and promoting choices of central banks to assist their very own currencies”.
But, the dimensions of the US bond market coupled with the shortage of a major, risk-free euro bond market implies that the US greenback will stay dominant.
The Europeans could lengthy for the euro to turn into a dominant forex however the nature of the financial structure and the obsession with pushing accountability for debt-issuance on Member State governments and an aversion to issuing EU-level debt backed by the ECB makes it exhausting for them to realize their targets.
The hope for the Europeans is that the Trump-induced chaos will compromise the so-called ‘protected haven’ standing of the US greenback.
The latest slide within the US greenback trade price will see an extra decline within the share of the US greenback in international reserve balances.
However the query is whether or not the tariff hoopla and the remainder of the ‘failed state’ meanderings of Trump and his cronies goes to trigger a structural decline within the US greenback.
Be aware: US Border Management officers – I’m not planning any journeys to the US within the close to future!
There’s some proof to assist the case that instances have modified.
As I famous above, when international uncertainty will increase the demand for US-dollar property (resembling authorities bonds) enhance.
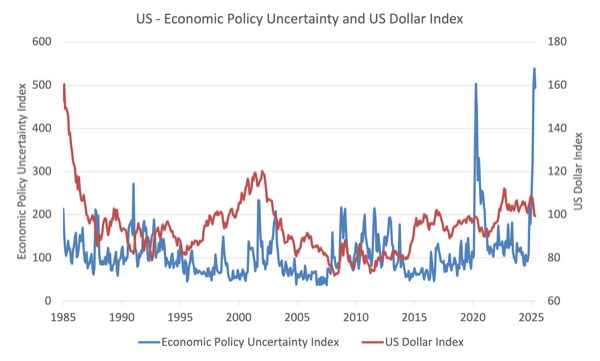
This graph compares actions within the month-to-month US Greenback Index (DX-Y.NYB) with the – US Financial Coverage Uncertainty Index from January 1985 to Might 2025.
Previous to 2025, there’s a pretty nicely outlined optimistic relationship between the 2 – when uncertainty rises, the greenback index rises (the exception being the lagged impact within the early COVID-19 interval).
Nevertheless, within the latest interval, that relationship has modified and the Trump uncertainty spike is past even the COVID-19 shock and the US greenback index is beginning to fall.
These findings are supported by extra formal econometric evaluation – HERE.
The EPU Index shouldn’t be accessible for June 2025 as but, however the US greenback index continues to fall into June – 2.5 factors round since finish of Might.
The ultimate level at this time is about what this implies for US fiscal coverage viability.
One of many accompanying narratives of the declining share of the US in international reserve balances is that the American authorities will begin to battle to ‘fund’ its fiscal deficit.
These claims that are being repeatedly rehearsed within the media as of late are with out basis.
As common readers will respect, the US authorities ‘funds’ its deficit within the act of spending, as a result of it’s the forex issuer.
No quantity of accounting buildings which are put in place can change that reality.
When the federal government instructs its monetary company to credit score a checking account to facilitate procurement necessities the quantity so typed is ‘funded’ at that time.
The quantity doesn’t replicate taxes or bond issuing income.
These numbers are, on this context, simply artefacts of the accounting techniques that the federal government makes use of to faux they’re ‘spending’ taxpayers or investor funds.
That isn’t to say that personal US merchants and so on is not going to be damage by the sliding significance of the US greenback in international markets.
They get pleasure from advantages resembling an absence of hedging insurance coverage outlays on transactions denominated in US {dollars}.
Conclusion
However the newest IMF and ECB knowledge and evaluation doesn’t recommend these benefits are about to dissipate any time quickly, even with Trump going loopy.
And on the declare that MMT is just relevant to the US due to its dominant standing as a reserve forex – I mentioned that proposition on this weblog submit – One other fictional characterisation of MMT finishes in whole confusion (March 13, 2019).
That’s sufficient for at this time!
(c) Copyright 2025 William Mitchell. All Rights Reserved.